Phytochemical mix PB125 Activates the Nrf2 Pathway reulting in Cellular Protection against Oxidative Stress
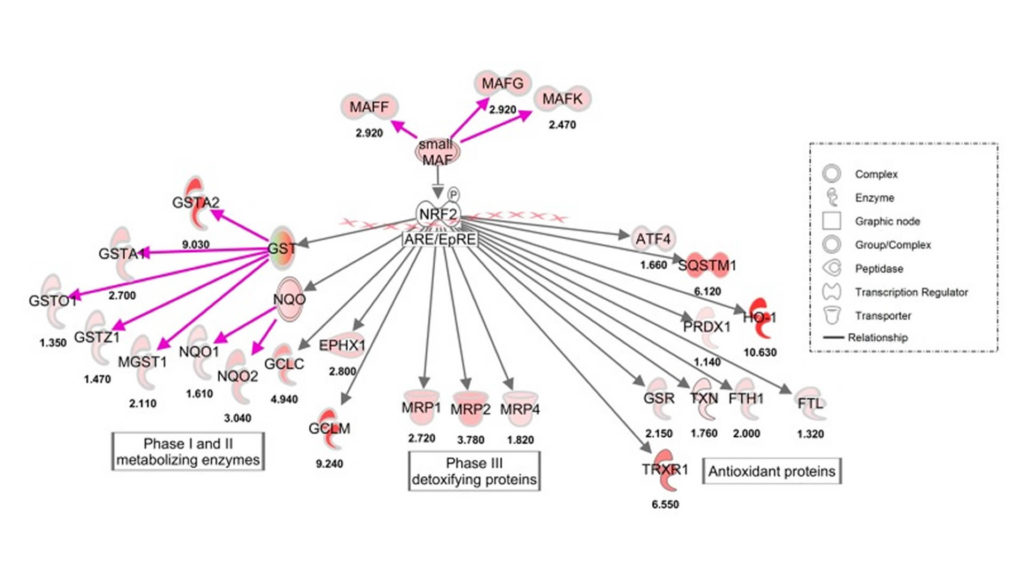
Bioactive phytochemicals at Rosmarinus officinalis, Withania somnifera, and Sophora japonica have a very long history of human usage to promote wellbeing. In this research we analyzed the ramifications of a blend of extracts from such plant resources based on specified amounts of the carnosol/carnosic acid, withaferin A, and luteolin amounts, respectively. These bioactive compounds have been demonstrated to trigger the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) transcription factor, which binds to the antioxidant response element (ARE) and modulates the expression of a vast array of cytoprotective genes. We found that mixtures of those three plant extracts act synergistically to activate the Nrf2 pathway, and we found that an optimized blend of the 3 representatives that we called PB125 to be used as a nutritional supplement. Using microarray, quantitative reverse transcription-PCR, and RNA-seq technology, we analyzed the gene expression caused by PB125 in HepG2 (hepatocellular carcinoma) cells, such as canonical Nrf2-regulated genes, noncanonical Nrf2-regulated genes, and enzymes that seem to be modulated by non-Nrf2 mechanics. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis identified Nrf2 as the key pathway for gene expression varies by PB125. Pretreatment using PB125 protected cultured HepG2 cells from an oxidative stress barrier brought on by cumene hydroperoxide vulnerability, by both cell viability and cell harm dimensions. Each component results in the stimulation of the Nrf2 pathway in specific ways, which contributes to upregulation of cytoprotective genes and defense of cells from oxidative stress and encourages the usage of PB125 as a nutritional supplement to promote wholesome aging.
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6563026/